Understanding the Principle of Differential Pressure Transmitters in Industrial Applications
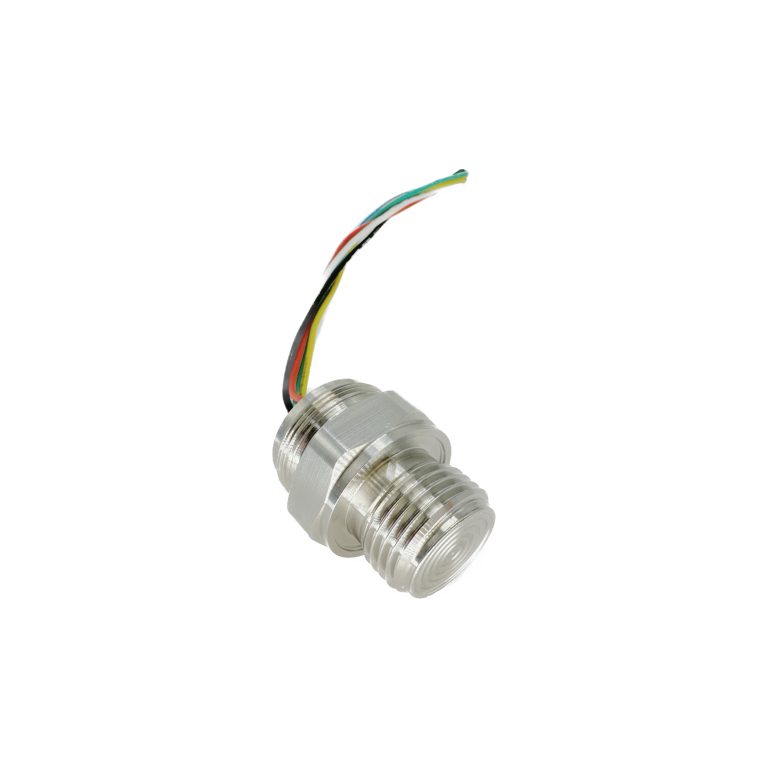
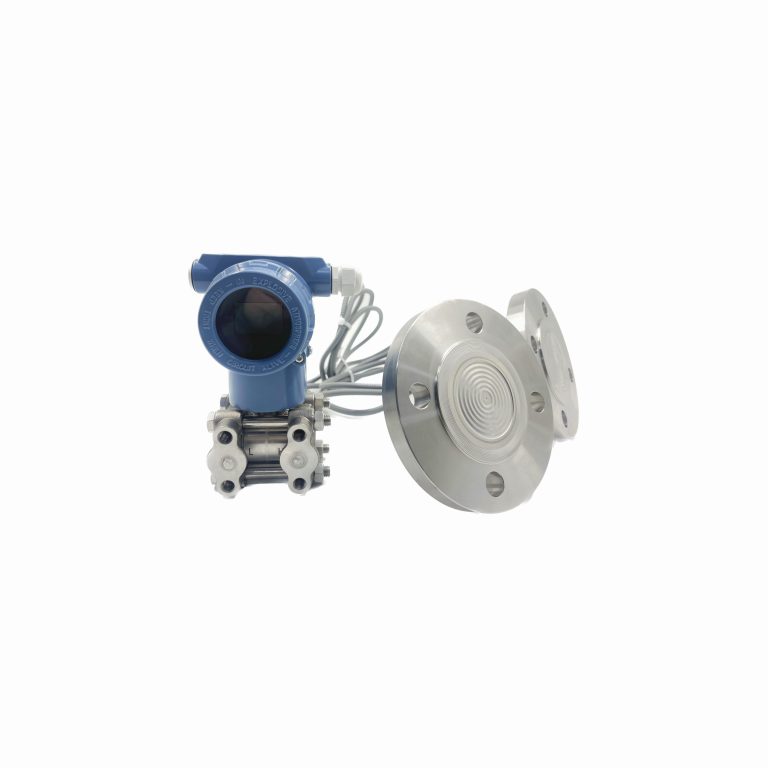
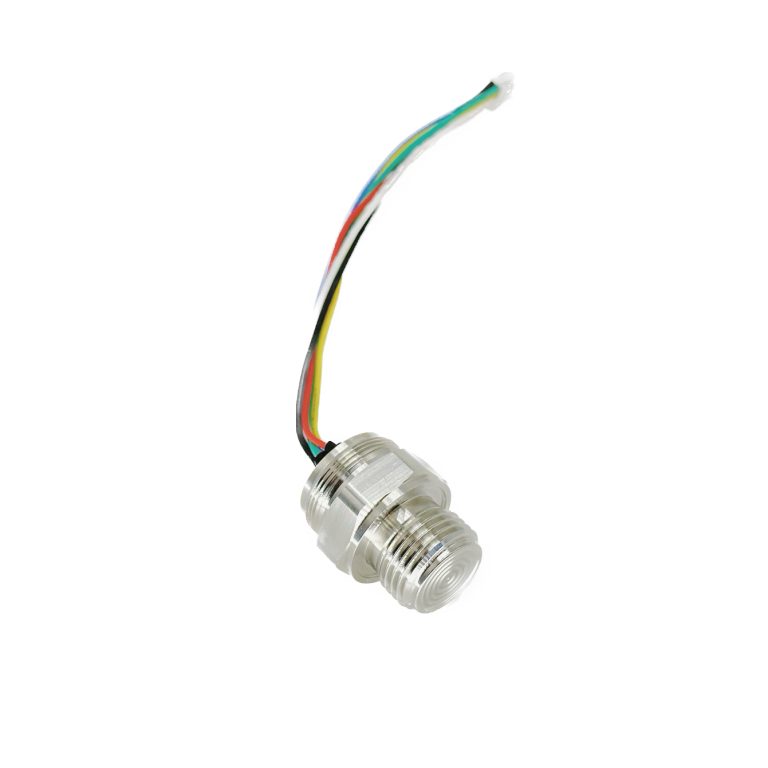
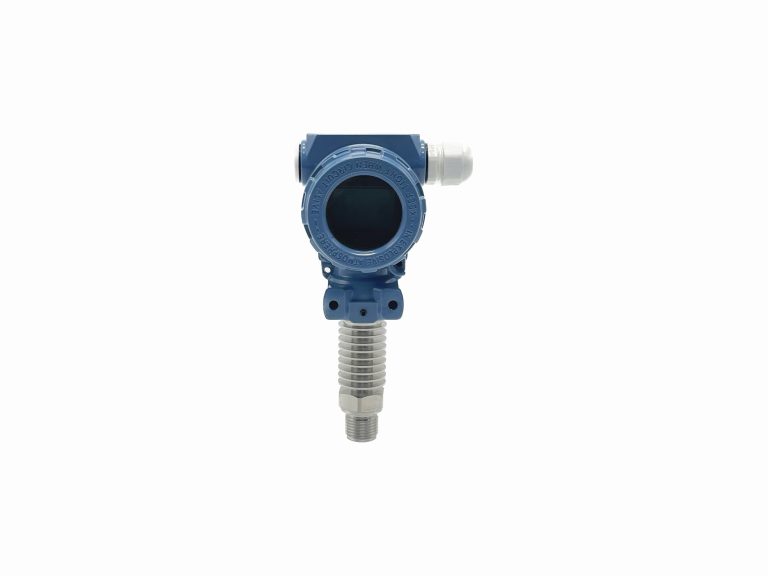
Differential pressure transmitters play a crucial role in various industrial applications. These devices are designed to measure the difference in pressure between two points in a system. By understanding the principle of operation of differential pressure transmitters, one can gain valuable insights into their functionality and importance in industrial settings. At its core, a differential pressure transmitter consists of a sensing element, a transmitter, and a process connection. The sensing element is responsible for detecting the pressure difference, while the transmitter converts this information into an electrical signal that can be easily measured and monitored. The process connection, on the other hand, allows the transmitter to be connected to the system being monitored. The principle of operation of a differential pressure transmitter is based on the concept of Bernoulli’s equation. According to this equation, the pressure difference between two points in a fluid system is directly proportional to the velocity of the fluid and the height difference between the two points. This principle forms the foundation for the functioning of differential pressure transmitters. When a fluid flows through a pipe or a vessel, it experiences a change in velocity and height. This change in velocity and height results in a difference in pressure between two points in the system. The sensing element of the differential pressure transmitter is designed to detect this pressure difference. The sensing element typically consists of two pressure chambers connected by a diaphragm. As the pressure difference between the two chambers changes, the diaphragm flexes, causing a change in the resistance of a strain gauge attached to it. This change in resistance is then converted into an electrical signal by the transmitter.
| Measuring medium | Gases, vapours, liquids |
| Inaccuracy | ±0.075% |
| stability | ±0.1%/3 years |
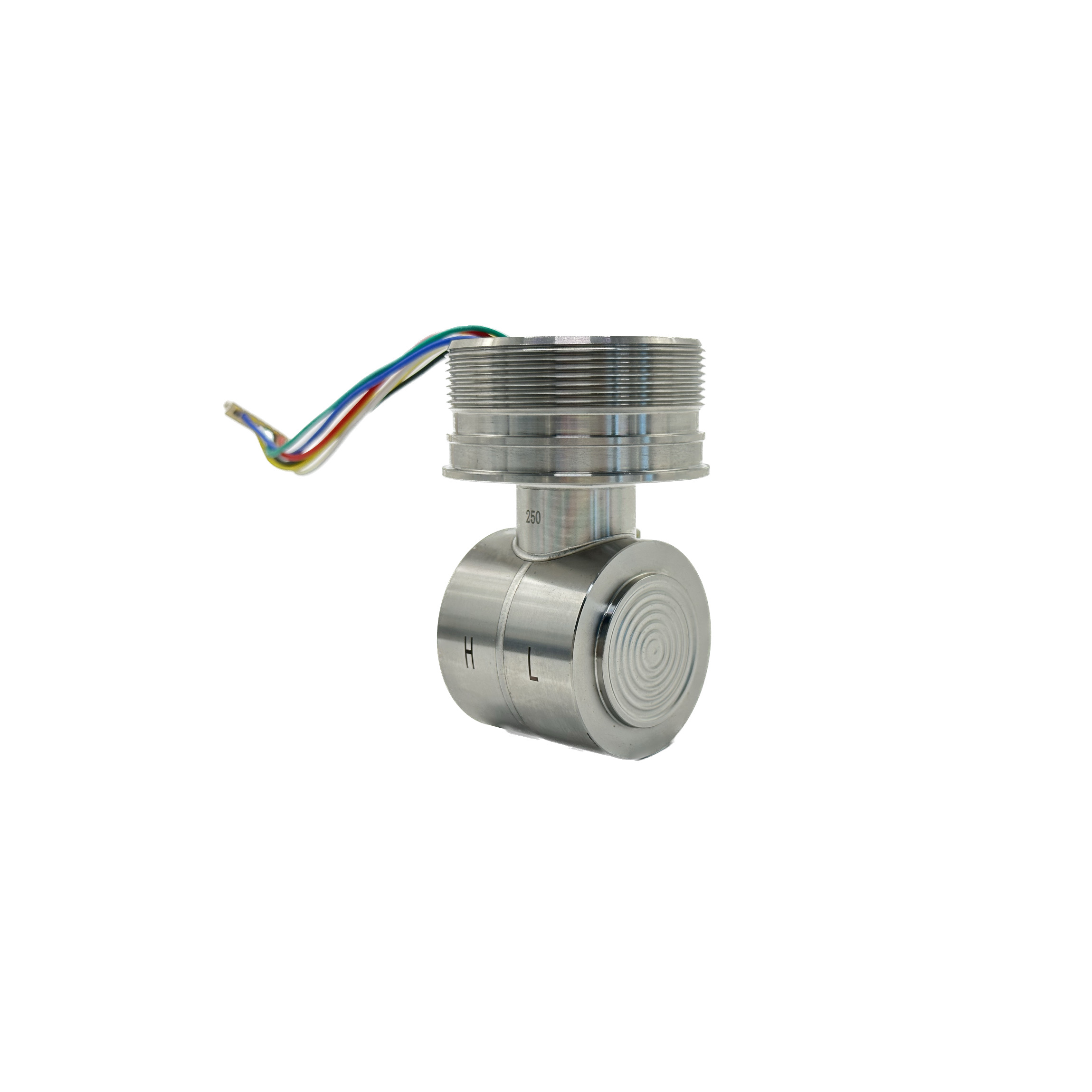 In industrial applications, differential pressure transmitters are used for a wide range of purposes. They are commonly used to measure flow rates, level, and pressure in various systems. For example, in a HVAC system, a differential pressure transmitter can be used to measure the pressure difference across an air filter, indicating the need for maintenance or replacement.
In industrial applications, differential pressure transmitters are used for a wide range of purposes. They are commonly used to measure flow rates, level, and pressure in various systems. For example, in a HVAC system, a differential pressure transmitter can be used to measure the pressure difference across an air filter, indicating the need for maintenance or replacement.





